Basic
Environment Name - A descriptive name for this environment, i.e. Dataweavers - Production
Environment Type - Either production or non-production. Default: Non-production
Provider Configuration | XM Cloud
GraphQL API Key - API key used to authenticate GraphQL requests from Spark to the XMC endpoint.
Spark uses this API key to retrieve URL information for regeneration items. Experience Edge webhooks provide updates in the form of ID’s, however headless regeneration requires URL’s and paths.
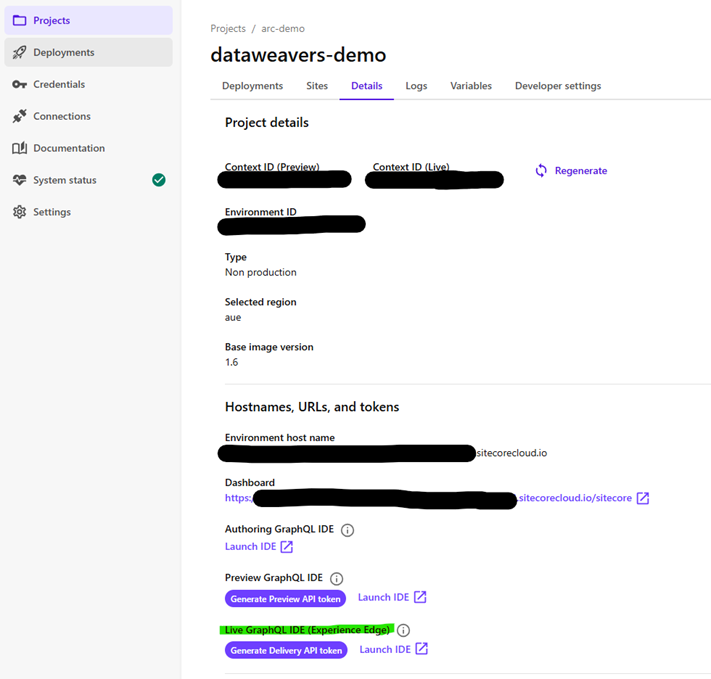
To retrieve the Experience Edge GraphQL API Key, navigate to the project and environment inside Sitecore AI. Click “Generate Delivery API Token” and copy the result into the Spark configuration app.
Admin Client Id – A Client ID for admin OAuth client used to manage XMC tokens.
Admin Client Secret - Secret for admin OAuth client.
Spark uses this API key and Secret to create and enable the Experience Edge webhooks for the platform.
Create the Client ID and Secret in the Sitecore AI Deploy application.
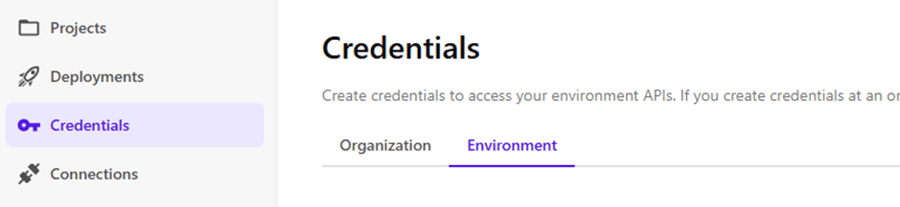
Create an Edge Administration credential and associate it to your current project and environment.
Allow Automated Updating Validation - If enabled, system can automatically validate token updates without manual steps.
Spark checks that the webhooks used to notify on publish are active and enabled and if they are disabled will re-enable. Why is this important? The Experience Edge publish webhooks can disable if requests continually fail or are deemed slow.
Edge - Basic
Edge Secret - Secret used for signing edge requests. When generating a new key, you must update your head application with the new value for Spark to remain functional.
This edge secret is used in your headless next.js application. If you’re using the Spark NPM package (https://www.npmjs.com/package/@dataweavers/spark-nextjs) then this value would be set in the SPARK_REGENERATION_SECRET environment variable.
Delete On Revalidate - If checked, stale cache entries are deleted before revalidation.
In a single regeneration process many pages could be regenerated, for example, if an entire site was republished and all pages were to be regenerated, then the application could experience throttling limits on Sitecore’s Experience Edge. To mitigate this issue, we allow the Spark process to regenerate as many pages as is allowed in the configuration (see Advanced configuration) and any additional pages are deleted and will be regenerated on next request and therefore will contain the up-to-date content.
IMPORTANT: Delete On Revalidate will only work for next.js SSG pages that have fallback configured to true (https://nextjs.org/docs/pages/api-reference/functions/get-static-paths#fallback-true).
Edge - Advanced
Pages per payload request - How many pages we allow per payload request. Default: 50 (XMC: 10, XM: 50).
Update requests per publish to a single endpoint - How many requests for regeneration we send to the headless application. Paths not included in the updates will be sent as deletion requests from the headless application. Default: 50 (XMC: 10, XM: 50).
Regeneration update timeout per request (seconds) - The timeout value provided to each request that is sent to the headless endpoint per update. Default: 10 seconds.
Regeneration update failed retry attempts - The number of attempted retries per update per endpoint. Default: 3.
Regeneration update interval between requests (milliseconds) - The time between requests sent to the headless endpoints. This affects both retries and payload split requests. Default: 1000ms (1 second).
Regeneration update failure retry HTTP statuses - The HTTP statuses returned from the headless application that will ensure the process retries the request (comma-separated). Default: 408 (request timeout), 500 (server error), 504 (gateway timeout).
Allow parallel regeneration updates? - Allows the headless endpoints to be updated in parallel. This can increase the chance of hitting limits or putting source systems under too much load. Default: true.
Endpoints
Name - Human-friendly identifier for the endpoint; must be unique within this environment.
Endpoint URL - Absolute URL used for outbound calls or integrations. Must be a valid URL.
This is the URL that the ODISR function will request, on the headless rendering application, when regenerating. This will be https://{rendering-domain}/api/dataweavers/odisr if using the Dataweavers supplied Spark NPM module.
Sites
Site Name - A name relevant to the CMS site. The incoming payload will contain a site name and only payloads with associated site names will be processed.
Hostname - The target/public facing hostname of the site.
Site Path Prefix* - The path prefixed to the incoming relative URL paths when sent for regeneration. This is to support frameworks such as next.js's handling of locales and multisite.
For example, in a Sitecore JSS multisite supported environment, the incoming URL might be /about-us/privacy-policy. With a "Site path prefix" value of /{locale}/_site_{sitename} (assuming a default locale of "en" and a site name of "testsite") the value sent to the host application for regeneration would be /en/_site_testsite/about-us/privacy-policy.
Supported Tokens:
- {locale} - the locale segment used in the generated path
- {sitename} - the sitename for this site
The path prefix is important and allows Spark to target the correct files when regenerating and deleting pages. When omitted it defaults to "/{locale}/_site_{sitename}".
Root Path - The content root path of the site in the CMS (e.g., /sitecore/content/mysite).
Automatically extracted from XM Cloud during subscription activation.
Virtual Path – A site’s virtual path, i.e. suffixed onto the domain.
Sitecore headless does not support this OOTB therefore this can be left empty, unless the default behaviour has been modified.
Default Language/Locale - The default locale code for the site (e.g., en, en-US).
Automatically extracted from Sitecore AI Cloud during subscription activation.
Locales - Comma-separated list of supported language codes for the site (e.g., en,fr,de).
Automatically extracted from XM Cloud during subscription activation.
Post Actions - Cloudflare Provider
Name - Display name for this provider.
Zone Id - Cloudflare zone identifier from your zone overview page.
Purge Type - Purge by URL or by only tagged items.
Cache Tag - Prefix for cache tags (if ByTag is used in the Purge Type).
Batch Size - Number of items queued before processing. Defaults to 500 if unset.
Retry Attempts - Number of retry attempts when purge fails. Defaults to 0 if unset.
API Key – The API key with appropriate permissions to purge the Cloudflare cache through the REST API.
Post Actions - Common Provider
Endpoint URL - URL for the Spark application to send a request to to content delivery endpoint.
Endpoint Headers - Request headers sent to the endpoint. Use key/value rows; empty rows are ignored.
Endpoint Auth (Basic/Token) - The token used to secure the endpoint.
Request Timeout (seconds) - Maximum request duration in seconds.
Batch Size - Number of items queued before processing. Defaults to 500 when unset.
Retry Attempts - Number of retry attempts when delivery fails. Defaults to 0 when unset.











